Serum Osmol Formula
The formula for calculating serum osmolality is: 2(Na) + Glucose/18 + BUN/2.8. Serum osmolality is an important measure of solute concentration in the blood.
Serum Osmol Formula It helps assess hydration status and kidney function. Understanding serum osmolality levels can provide valuable insights into a patient’s overall health and guide appropriate medical interventions. Abnormal serum osmolality can indicate conditions such as dehydration, overhydration, or kidney dysfunction. Monitoring serum osmolality is crucial in managing various medical conditions and ensuring optimal patient care.
By utilizing the serum osmol formula, healthcare providers can make informed decisions to maintain proper fluid balance and support overall well-being.
The Essence Of Serum Osmolality
The essence of Serum Osmolality lies in its vital role in measuring the concentration of solute particles in the blood. Understanding the components and regulation of osmolality is crucial for maintaining proper hydration levels and overall health.
Key Components In Osmolality Measurement
- Solutes like sodium, glucose, and urea
- Water content in the blood
- Measuring units in milliosmoles per kilogram (mOsm/kg)
Hydration’s Role In Osmolality Regulation
- Balances solute concentration in the blood
- Affects osmoreceptors in the brain
- Ensures proper fluid levels in the body

Credit: www.researchgate.net
Serum Osmol Formula Explained
The Serum Osmol Formula is a vital tool in understanding the concentration of solutes in the blood. By delving into the intricacies of this formula, we can gain valuable insights into the body’s osmotic balance and overall health. In this section, we will explore the Serum Osmol Formula, including how to calculate serum osmolality and the factors that affect the formula’s accuracy.
Calculating Serum Osmolality
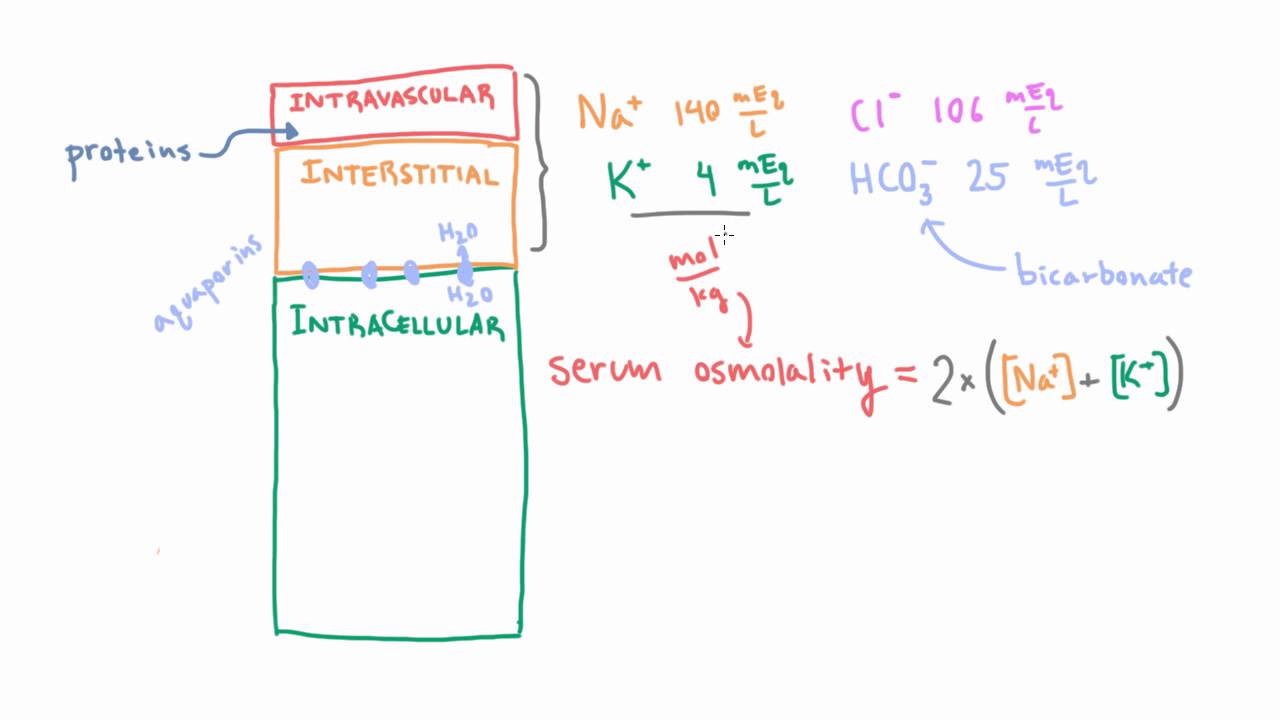
The calculation of serum osmolality involves a straightforward formula: Serum Osmolality (mOsm/kg) = 2[Na] + Glucose/18 + BUN/2.8. This formula takes into account the concentrations of sodium, glucose, and blood urea nitrogen (BUN) in the serum. By plugging in the respective values for each component, healthcare professionals can obtain a crucial measure of osmotic activity in the blood.
Factors Affecting The Formula’s Accuracy
Several factors can impact the accuracy of the serum osmol formula. These include variations in laboratory techniques, the presence of other substances in the blood, and the potential for analytical errors. It’s essential for healthcare providers to be mindful of these factors when interpreting serum osmolality results, ensuring that the data accurately reflects the patient’s physiological state.
Clinical Significance Of Serum Osmolality
Serum osmolality is a crucial measure of the body’s electrolyte and water balance, calculated using the formula: 2(Na) + Glucose/18 + BUN/2. 8. It helps in diagnosing and managing various clinical conditions such as dehydration, hyponatremia, and diabetes insipidus. Regular monitoring of serum osmolality is essential for patient care and treatment planning.
Serum osmolality is an important parameter that helps in determining the hydration status and electrolyte balance of an individual. It is a measure of the concentration of solutes in the blood and is expressed in terms of milliosmoles per kilogram (mOsm/kg). The normal range for serum osmolality is between 280-300 mOsm/kg. Deviations from this range can indicate various medical conditions and can have serious consequences if left untreated.
Diagnosing Hydration And Electrolyte Imbalances
Serum osmolality is an important tool in diagnosing hydration and electrolyte imbalances. A low serum osmolality indicates overhydration or hyponatremia, while a high serum osmolality indicates dehydration or hypernatremia. In cases of dehydration, the body loses more water than it does electrolytes, which results in an increase in serum osmolality. On the other hand, in cases of overhydration, the body retains more water than electrolytes, leading to a decrease in serum osmolality. By measuring serum osmolality, medical professionals can determine the hydration status of an individual and take appropriate steps to correct any imbalances.
Monitoring Therapeutic Interventions
Serum osmolality is also used to monitor the effectiveness of therapeutic interventions in treating various medical conditions. For example, in cases of diabetic ketoacidosis, the goal of treatment is to reduce serum osmolality by replacing fluids and electrolytes. By monitoring serum osmolality, medical professionals can determine the effectiveness of treatment and adjust the therapy as necessary. Similarly, in cases of water intoxication, the goal of treatment is to increase serum osmolality by removing excess water from the body. Serum osmolality measurements can help in monitoring the effectiveness of treatment and preventing complications. In conclusion, serum osmolality is an important clinical parameter that can help in diagnosing and monitoring various medical conditions related to hydration and electrolyte imbalances. By measuring serum osmolality, medical professionals can take appropriate steps to correct any imbalances and ensure optimal patient outcomes.
Interpreting Serum Osmolality Results
Understanding High And Low Values
Serum osmolality is a measure of the concentration of solutes in the blood. High serum osmolality may indicate dehydration, diabetes, or certain kidney disorders, while low serum osmolality can be a sign of overhydration, adrenal insufficiency, or excess water intake. It is essential to consider the patient’s clinical condition and other laboratory values to interpret serum osmolality accurately.
Case Studies: From Numbers To Diagnosis
Case 1: A patient presents with elevated serum osmolality and symptoms of extreme thirst and dry mouth. Further investigation reveals hyperglycemia, leading to a diagnosis of uncontrolled diabetes mellitus.
Case 2: A patient exhibits decreased serum osmolality along with confusion and lethargy. Laboratory findings show low sodium levels, indicating possible hyponatremia due to excessive fluid intake.
Hydration Metrics And Health
Hydration is crucial for maintaining overall health and well-being. The balance of water in our bodies is regulated by various metrics, including osmolality, which measures the concentration of solutes in body fluids. Understanding the role of osmolality in body water balance and identifying optimal hydration levels for different populations is essential for promoting good health.
The Role Of Osmolality In Body Water Balance
Osmolality refers to the concentration of solutes, such as sodium and glucose, in body fluids. This metric plays a critical role in regulating the movement of water between different compartments of the body. Maintaining optimal osmolality is essential for ensuring proper hydration and supporting various physiological functions, including fluid balance, nerve function, and kidney health.
Optimal Hydration For Different Populations
Infants and young children have different hydration needs compared to adults, as their bodies have higher water content and metabolic rates. Similarly, elderly individuals may be more susceptible to dehydration due to age-related changes in thirst perception and kidney function. Understanding the unique hydration requirements of these populations is important for promoting their health and well-being.
Advancements In Osmolality Measurement
Measuring serum osmolality is an essential diagnostic tool used in various clinical settings. It is a quantitative measurement of the concentration of dissolved particles in a patient’s serum. The serum osmolality reflects the balance between electrolytes and water in the body. Any disruption in this balance can lead to serious medical conditions. The osmolality measurement is particularly useful in diagnosing and monitoring patients with dehydration, renal dysfunction, and other electrolyte imbalances.
Innovations In Laboratory Techniques
The traditional method of measuring serum osmolality is time-consuming, requiring several steps and specialized laboratory equipment. However, recent advancements in laboratory techniques have made the process faster and more accurate. Automated osmometers are widely used in laboratories to measure serum osmolality. These automated osmometers use a freezing point depression method to measure serum osmolality, which is a more precise method than the traditional method.
Point-of-care Devices And Their Impact
Point-of-care (POC) devices are portable instruments that allow physicians to perform diagnostic tests at the patient’s bedside. These devices have revolutionized healthcare by providing rapid and accurate results, eliminating the need for sending samples to a laboratory. Several POC devices have been developed to measure serum osmolality, including handheld osmometers and microfluidic devices. These devices are easy to use, require only a small amount of sample, and provide results within minutes. The use of POC devices has significantly improved patient care by allowing for quick diagnosis and treatment.
In conclusion, advancements in osmolality measurement have had a significant impact on patient care. Innovations in laboratory techniques and the development of POC devices have made the measurement of serum osmolality faster, more accurate, and more accessible. These advancements have improved the diagnosis and treatment of various medical conditions related to electrolyte imbalances, dehydration, and renal dysfunction.
Practical Applications In Sports And Fitness
When it comes to sports and fitness, Serum Osmol Formula offers practical applications that can revolutionize hydration strategies for athletes. From tailoring hydration plans to optimizing performance and recovery, understanding osmolality is crucial for achieving peak physical condition.
Tailoring Hydration Strategies For Athletes
Athletes have unique hydration needs that require a personalized approach. By incorporating Serum Osmol Formula, trainers and coaches can tailor hydration strategies based on individual osmolality levels, ensuring optimal performance and reducing the risk of dehydration-related issues.
Osmolality In Performance And Recovery
Understanding osmolality is essential for enhancing athletic performance and expediting recovery. By monitoring osmolality levels and adjusting hydration plans accordingly, athletes can maintain optimal fluid balance, prevent cramping, and accelerate post-exercise recovery, ultimately improving overall performance.
Dehydration And Overhydration: Prevention And Management
Dehydration and overhydration are critical conditions that require proper prevention and management strategies. Understanding the risk factors and symptoms, as well as adopting effective hydration practices, play a key role in maintaining optimal serum osmolality levels.
Identifying Risk Factors And Symptoms
Risk Factors: Poor fluid intake, excessive sweating, vomiting, diarrhea, and certain medications increase the risk of dehydration or overhydration.
Symptoms: Thirst, dry mouth, fatigue, dizziness, dark urine (dehydration); swelling, confusion, nausea, and seizures (overhydration).
Effective Hydration Practices
- Drink water regularly throughout the day.
- Monitor urine color to assess hydration status.
- Avoid excessive intake of sugary or caffeinated beverages.
- Consume fruits and vegetables with high water content.
Future Perspectives In Hydration Science
Recent studies show promising trends in understanding the impact of osmolality on hydration.
Advancements in technology pave the way for personalized hydration solutions tailored to individual needs.

Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Formula For Calculating Osmolarity?
To calculate osmolarity, use the formula: Osmolarity = (Molarity of solute) x (Number of particles formed when solute dissolves).
What Is The Formula For Serum Osmolality Ncbi?
The formula for serum osmolality according to NCBI is: Osmolality = 2(Na) + Glucose/18 + BUN/2. 8. This formula calculates the concentration of solutes in the blood serum.
What Is The Solution Serum Osmolality?
Serum osmolality solution refers to the concentration of particles in the blood. It is an important measure of kidney function and hydration status.
What Is The Formula For Serum Osmolarity In Hhs?
The formula for serum osmolarity in HHS is calculated by adding the sodium and glucose levels, then dividing by 18.
Conclusion
Understanding the Serum Osmol Formula is crucial for maintaining proper hydration and overall health. By calculating serum osmolality, healthcare professionals can assess a patient’s fluid balance and make informed treatment decisions. This simple yet essential formula plays a significant role in clinical practice and patient care.







